Intro If you have lint compliants as following when using ESLint( and plugins likeeslint-plugin-prettier) with Prettier, read this article. or Use semicolons in JavaScript In JavaScript, it is not mandatory to use a semicolon at the end of each line. However, I am opinionated with a semicolon to end each statement explicitly. I don't want to argue which is better. If you do not enforce semicolon usage (or omission) in any particular way, ignore this article. Code formater and beautifier tool Prettier is sticky to this style and enabled semi to true by default. Meanwhile, we usually combine a linter tool like ESLint to do static code checker, but ESLint has its own rules to format code which may not be consitent with Prettier. Different default semi rules However, ESLint's recommended rules don't like semicolons, and don't allow semicolons at the end of the code lines, and overrides Prettier's semi option setting. In the other word, the ASI(Automatical Semicolon Insertion) will not work even when we turn on Prettier's semi option as ESLint recommended rules turns it off by default. They conflict with each other. While using them together: When we run eslint to check the code, complaints come out as Prettier still expects semicolons while ESLint supressing the semicolons. This is really annoying. Turn on ESLint's semi rule So, what about turning on ESLint's semi rule in eslintrc.js? Yes, ASI is enabled, however, the linter still complains: The tooltip will appear on each semicolon after I apply the semi rule in the config file. I guess(I am not sure)…
Redux Redux is a predictable state container for JavaScript apps. As state in application becomes increasingly complicated for SAP, there might be more different types of state to manage: local created data which is not persisted to the server, UI data like UI elements properties, routes, spinners, paginations which determines the UI display; and server returned and cached data, etc. Redux attempts to make state mutations predictable for complicated application state by imposing certain restrictions on how and when updates can happen. These restrictions are reflected in the three principles of Redux. Three principles of Redux Single source of truth for application state: The global state of application is stored in an object tree within a single store; State is read-only: The state cannot be modified directly by views or network callbacks, the right way to mutate is to dispatch an action to notify the reducer to process. As all changes are centralised and happen one by one in a strict order, there are no subtle race conditions to watch out for; Changes are made with pure functions: Change state via reducers. A reducer is a pure function with two characteristics: It returns same result when the input parameters are the same; the only dependency of the returned data are the input parameters, and the result is consistent regardless of where/when it is called. no side-effects: the function will not do jobs like: modify external data, render DOM elements, execute network requests, IO operations. These characteristics provides assurance to make state predictable. Three core concepts of Redux Actions: an action…
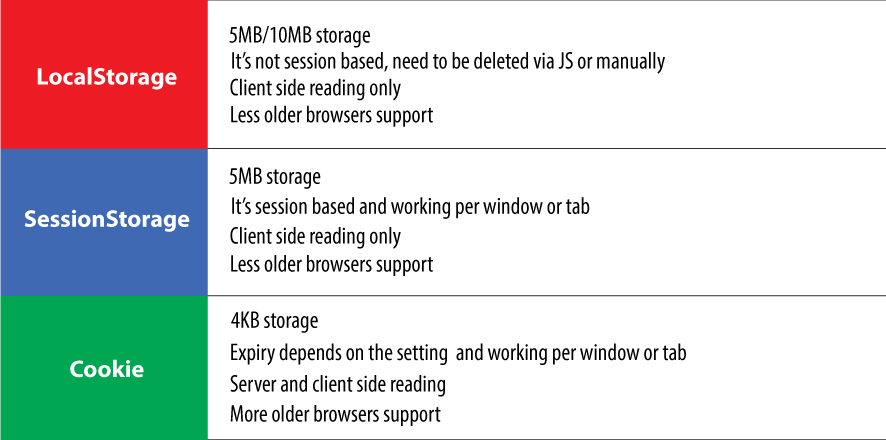
Ways to share data between Vue components without middleware component props: parent --> child $parent, $child, ref and $refs: access parent, child or referred component data emit events: child (this.$emit('event_name', data)) ---> parent ( @event_name="eventHandler") $attrs/$listeners: pass comoponent props(v-bind) or events(v-on) downside level by level provide/inject: ancient component provides shared data for all the descendant components to use. Event Bus, $emit and $on: use an empty Vue instance as the global shared event bus. By means of events carried by the event bus, parent, child, sibling components can share data without restriction. or add Event Bus to Vue prototype property in main.js Web Storage API: HTML5 provides localStorage and sessionStorage API for data persistance for different scale and period. Thus, the page components can call these APIs to read/write data for sharing. slot-scope: Put slot-scope into template tag, and bind the template with data exposed by the child component. This allows the parent to render child component with different UI styles or data by the template slot. By this way, the parent component can used data inside the child component and render it with styles from parent itself. This is a very limited scope data sharing between parent and child components. Why and When to use Vuex? Ways to communicate between components mentioned above can be used according to different rscenarios. Some ways are strictly restricted by components relationship and are not flexible for global data sharing; Athough the Event Bus provides a lightweight way for share data globally, it's not easy to manage events and state when it's used…
The official definition of GraphQL: A query language for your API. GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data. GraphQL provides a complete and understandable description of the data in your API, gives clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more, makes it easier to evolve APIs over time, and enables powerful developer tools. My underdtanding of GraphQL The initial impression of GraphQL to me is that it is one type of SQL language for images, however, this is completely wrong after I read the docs, and I get a better understanding of it by doing some practice. It's not used for picture/images queries, it is just a new open-source data query and manipulation language for APIs, originally developed by facebook. Most of developers know the popular REST API, and there are also other types of API specifications like JSONAPI, SOAP as well. GraphQL query language is used by clients to query data from a GraphQL API service. It's a API query language, not a database query language like SQL. Thus, it doesn't mean that the client uses GraphQL to query data from a database, it queries data from the GraphQL service. It's also a runtime, this means GraphQL can play a role as a server-side service layer for executing the client queries, by using a type system defined for the data. In fact, it isn't tied to any specific database or storage engine and is instead backed by the existing code and data at…
ECMAScript 2020, the 11th edition, introduces the Promise.allSettled, a new Promise combinator that does not short-circuit; And Promise.any is scheduled to be supported in ES2021 standard. The two new features are inroduced five years after Promise.all and Promise.race functions which were introduced in ES6(2015). The four combinator functions will make a more complete implementation of Promise for different asynchronous use cases. Status of a Promise A settled promise means that it is not pending, i.e. it is either fulfilled or rejected. Promise.all The Promise.all() method takes an iterable of promises as an input, and returns a single Promise that resolves to an array of the results of the input promises. This returned promise will resolve when all of the input's promises have resolved, or if the input iterable contains no promises. It rejects immediately upon any of the input promises rejecting or non-promises throwing an error, and will reject with this first rejection message / error. Promise.all will shortcut on the first rejected promise, so we cannot get any resolved data/status once a promise is rejected even when some promises have already been resolved. In order to get all the results(including status) of each promise after call Promise.all, we need to add a new function to return a new promise( promise.then() ), and return a new value with the status known in promise.then (either through the resolved branch or the rejected branch). Then iterate the results and filter the status after call Promise.all. Promise.allSettled The similarities and diffrences with Promise.all: They both receive an array of promises, and return a…
Scenario and issues If we have internal page data to update, we can implement it by calling component methods to update when the event is triggered, other than to do a whole page re-render. However, we need to call $router.push() method to navigate to a destionation page from another one, and this is my case: I make a component(a button) which is used in different pages to navigate to page A, the component calls $router.push() to jump to page A , Meanwhile, this component is also used iniside page A, that means it's internal route jump to update a part of content in page A; I use the named route with params binding the changed data page A needs in $router.push(). By this way, page A can always get data from the named route and doesn't need to take care of these two different types of navigation. But the issue comes: I cannot do an internal update of page A when the I trigger the component in page A; To watch $route or use beforeRouteUpdate hook to capture changes in page A is not working. The route navigation doesn't trigger these functions, even when the passed params are changed in push(). More details about $route.push() method After trying some ways I fixed this issue and found more details about push() method, which may not be clearly elaborated in the official docs. push() methods returns a promise, so we can catch the error to get reasons when it fails. By adding try catch, I got this: Error: Avoided redundant navigation to…
Use sessionStorage to fix page blank issue of F5 refresh due to vue route push params loss
I experienced the issue(mentioned in the article title) when using the push method of Vue router to redirect to a new URL when clicking on some anchors today. Usually, there are two typical ways to go to the new page(route) via using push method: The params passed by the first way(use params)will not be shown in the URL, so if we want to hide more details of the page, it's a better way. However, when I use this way, the web page turns out to be blank when I press F5 to update, as the page cannot get the route parameters which are used as data request params. The route params won't be persistant via this way, they will not exist when page reloads. This is becuase the named route is not pushed into history records, the browser is not able to find a record to reload. Ways to fix To fix this, we can use the second way(use query) to push route params and the parameters will persit even if a F5 update happens. However, the parameters will show up in the URL, and object parameters with several level-depth will turn into long garbled code. I don't want this as I hope to keep the URL address clean. How about the other ways to fix this? I tried to create another state in the Vuex store to keep the data, but this doesn't work as well unless I use the plugin vuex-persistedstate. I checked its github repo and find it uses localStorage, sessionStorage or cookie to persist data. so…
A Router is commonly known as a hardware device for computer networking, we all have wired or wireless routers at home, offices or other locations for devices networking. Router in Web Application We'll get different page content from a site when we change the string after the domain name in a URL, or click the menu items of a webpage. This navigation feature of web apps is done by a Router middleware of the modern web app as well. Accessing to a specific URL path will trigger a respective route response from the web app's routing table, the web app usually uses a specific Router middleware to manage all the routes, no matter whether the routing pages are rendered from server-side or client-side. For example: Backend routing: in Node.js, we can implement routes by express.js, and each endpoint will render the template to html for client-side, each time accessing to a new path(route), there will be a new request sent to the backend. Front-end routing: React.js and Vue.js have their own favorable routing middleware from their ecosystem: react-router and vue-router respectively. The front-end routing is always used for SPA(single page application) website, as it prevents un-neccessary requests to the server, the change of a route accessing will lead to only partial internal view change inside the page, which is usually related to a specific component view of the web app, and whole page rendering is avoided. Understanding Routing mechanism in SPA by Analogy We don't care whether it is called as a path, a uri, or a route when browsing…
Sass: Syntactically Awesome Style Sheets is the most mature, stable, and powerful professional grade CSS extension language in the world. 1. Steps to use sass in Native html Install sass globally by npm Create separate folders to put .scss and .css files Watch .scss files and compile them to .css real-time Monitor and sync compile single .scss file Monitor and sync compile .scss file to .css in its own directory Or use an extention in VsCode to compile: live-sass-compiler: Compile Sass or Scss to CSS at realtime with live browser reload. easy-sass: Built-in, easy to use Sass compiler Link the .css file in the header of html document: 2. Steps to use sass in React Install node-sass as dependency for React Change file extension .css to .scss Import the .scss files in React component: or read the React official tutorial here 3. Steps to use sass in Vue.js Install npm packages as development dependency: or setup to use them when creating Vue app via vue-cli scaffold tool. You can pick a preset manually and choose a CSS Preprocessor tool while running the vue-cli scalffold. If you choose SASS/SCSS, node-sass and sass-loader will be installed automatically when the project is created. Add lang="scss" in the style tag of the Vue component:
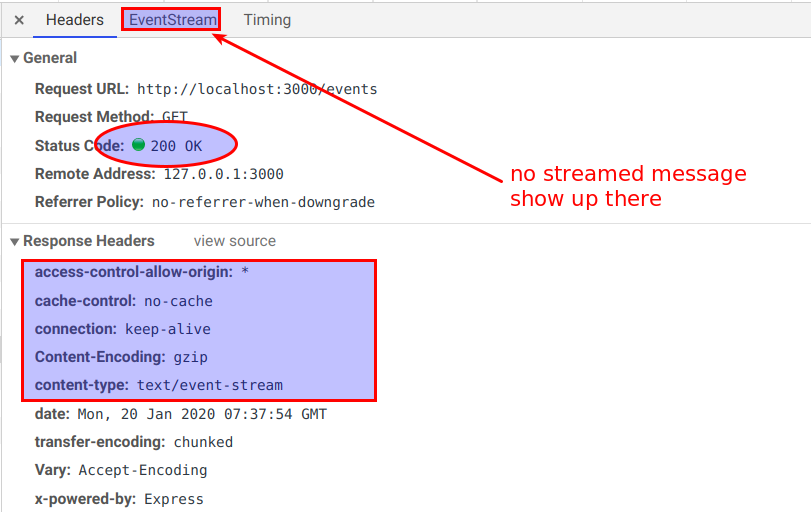
Issue and phenomenon When I use server sent events to the react client: the event messages can be received when I access the backend by request url directly from the browser address bar, but can never be received by the front end application, and the EventStream in Chrome Dev-Tool is empty; However, once I stop the backend server, ALL the messages are flushed/sent to the client at one time. It seems that the messageS are buffered or pended somewhere. The node.js/express test code: The client javascript: Analysis I have already enabled CORS by using cors middleware at the backend; The proxy works fine, as the other requests to the endpoints are avalaible; The Cache Control option settings of the response HTTP header of server-side are exactly the same with the sample code of MDN docs and it looks right. I didn't get an answer from others or google sse, eventSource, cors or proxy. One suggested way is to disable CORS of browser: $ google-chrome --disable-web-security But I don't think this is a good way as we need to put things online eventually, it didn't work for debugging as well when I tried. Solutions This bugged me serveral hours. I luckily found two solutions by changing code line by line: Use full URL to request the events (may not be decent, but it works) from client side: const sse = new EventSource('http://localhost:8080/events'); Set the server-side Cache Control Header to no-transform: 'Cache-Control': 'no-cache', --> 'Cache-Control': 'no-transform', or 'Cache-Control': 'no-cache', --> 'Cache-Control': 'no-cache, no-transform', I cannot fully understand why the no-transform directive matters…