
Intro
My computer is Lenovo T460p, upgraded after I bought in 2017:
- 480G SSD(Q200 Ex) : replaced the original HHD
- 24G RAM(8G+16G): increased a 16Gb Samsung RAM
It came along with an installed Windows 10 which I updated to version 1903 recently. A course I want to take doesn't support a machine with Windows friendly, it suggests a Ubuntu or Mac.
While we strongly recommend using an Apple Macbook for your laptop, we also understand that it's not exactly the most economical option. If you already own a Windows laptop, then you are expected to install and use Linux either alongside (dual boot) or instead of Windows. Ubuntu is our suggested vendor, but Mint is also a fair option.
However, I am not willing to install dual-boot systems or replace the already installed Windows 10, as my internal SSD is full of data, it's also not easy to find an economical M.2 2242 type SSD which can be extended on board as a second hard drive.
They suggest install Ubuntu on an external drive as an alternative option. It's a economic solution indeed after I found this SSD ( sale price: $99.99 at Best Buy/Amazon on Sept. 12th):
Preparation
- A 32 GB USB stick/flash drive (more than 4G is acceptable)
- Utility: Rufus.exe 3.7 Portable
- Ubuntu 18.04 Desktop Image
- Samsung T5 500G SSD with USB cable
Steps
1. Create a Ubuntu bootable USB stick
-
Win 10 is both compatible with UEFI and legacy BIOS boot mode. Run command
msinfo32to check boot mode; a Win 10 On SSD(GPT) usually boots from the UEFI mode,
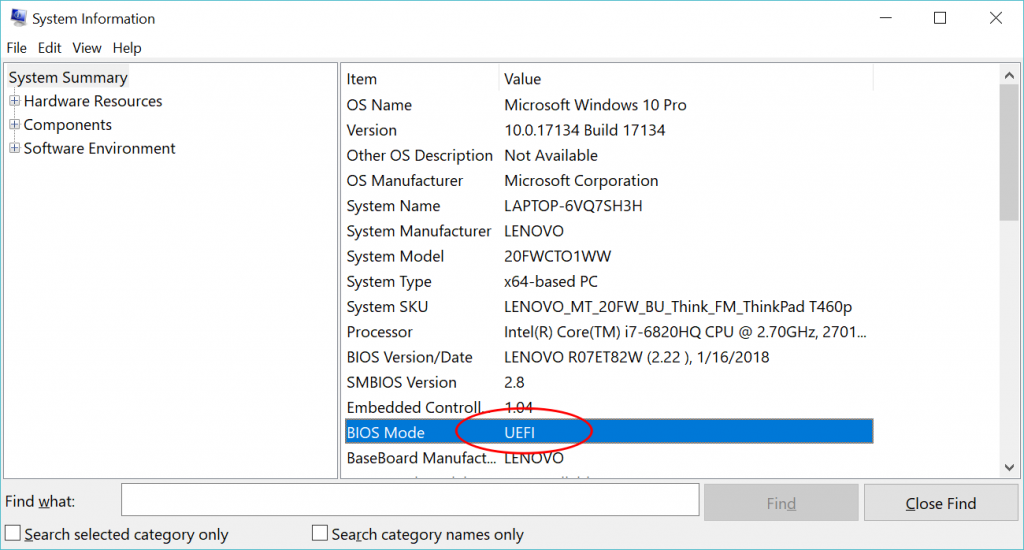
-
Insert the USB stick, and start Rufus program to create a bootable USB(the program will detect the USB stick automatically): select the downloaded Ubuntu Image, choose the Partition scheme as GPT/UEFI(non CSM). if your Win 10 runs from a legacy BIOS boot mode, just keep the default(MBR/Bios or UEFI). Then, click the Start button, wait until job done.
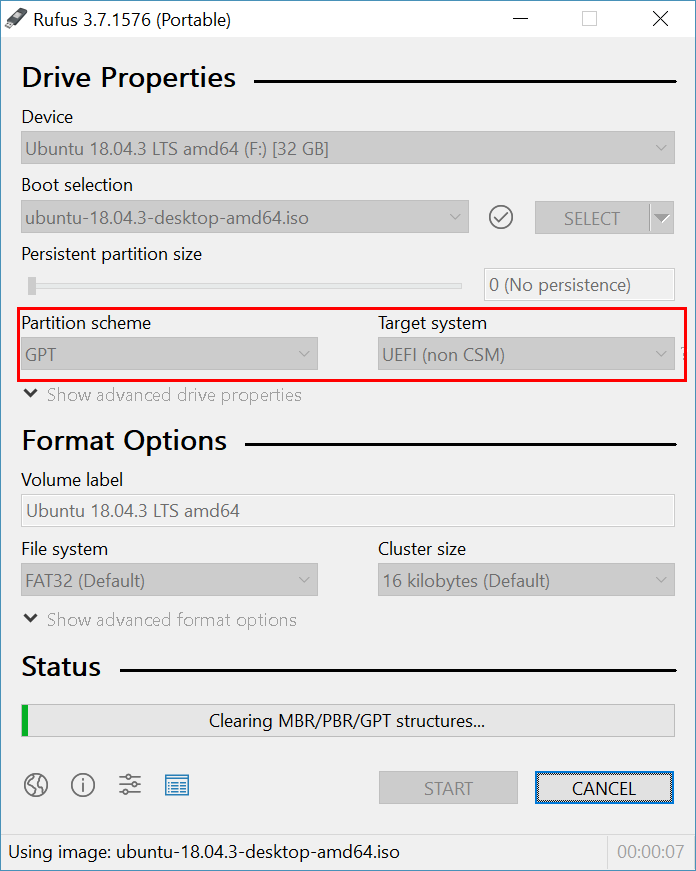
2. Restart to choose a boot device
Use USB cable to connect the new drive to T460p. Reboot the computer and press F12 immediately when the Lenovo Logo appears to enter boot device option(Windows Boot Manager). Choose USB HDD as the boot device and let the computer boots from the Ubuntu bootable USB stick.
3. Install the Ubuntu from USB stick
Then we can use the GUI installer to install Ubuntu on the new drive. If you connect the Internet when installing, pay attention when come to "updates and other software" option:
- Type of Installation: choose
Normal Installation - Do not tick
Install third party software for graphics and Wi-Fi ...... media formats, this will avoid Ubuntu from asking to disable secure boot.
When come to "Installation type" option: choose Something else and then part the new SSD drive. A New Partition Table on the external SSD should be created. Note that:
- DO NOT part the drive which Windows 10 already installed on wrongly
- A UEFI partition should be allocated separately when using UEFI(non CSM) boot mode
-
My partition table for the new drive (around 200G space allocated, and I only created three partitions to make it easier):
- Primary partitions
- UEFI: 1G
- /: 150G , ext4 file system
- Logical Partition
- swap area: 48G (two times of the RAM)
Ubuntu@T460p:~$ lsblk /dev/sdb NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdb 8:16 0 465.8G 0 disk ├─sdb1 8:17 0 1024M 0 part /boot/efi ├─sdb2 8:18 0 139.7G 0 part / ├─sdb3 8:19 0 44.7G 0 part [SWAP]
- Primary partitions
When the installation is completed, click "Restart Now", the computer will boot to a GRUB boot menu, the default boot system is Ubuntu, and Windows 10 on the internal drive is also in it.
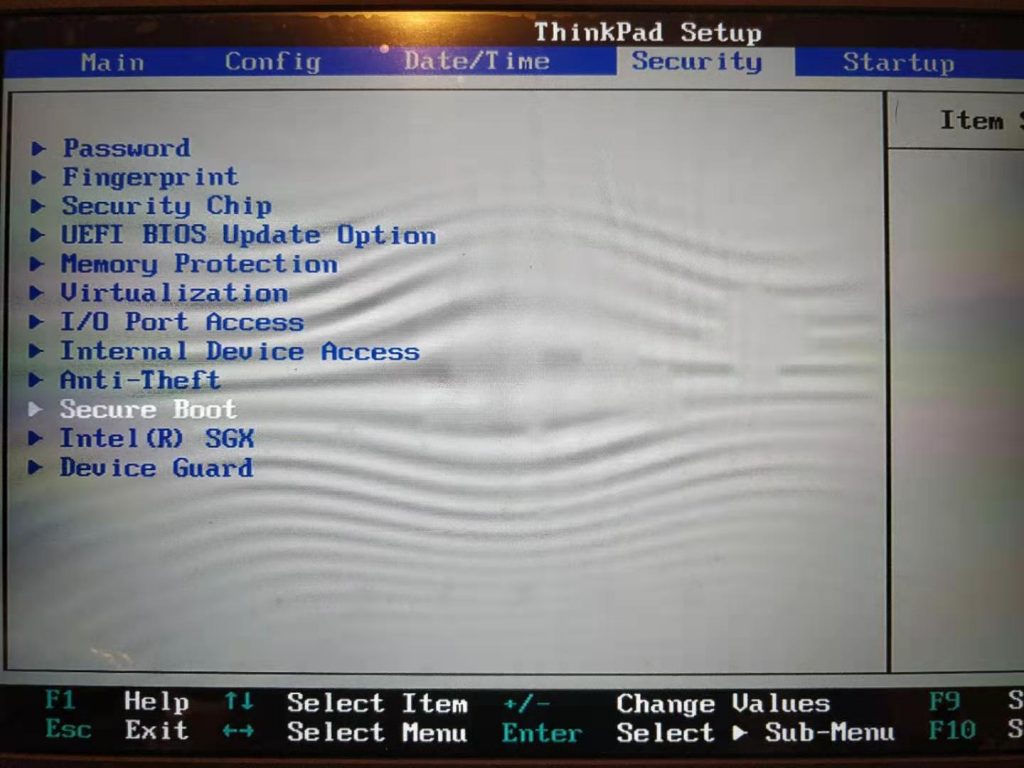
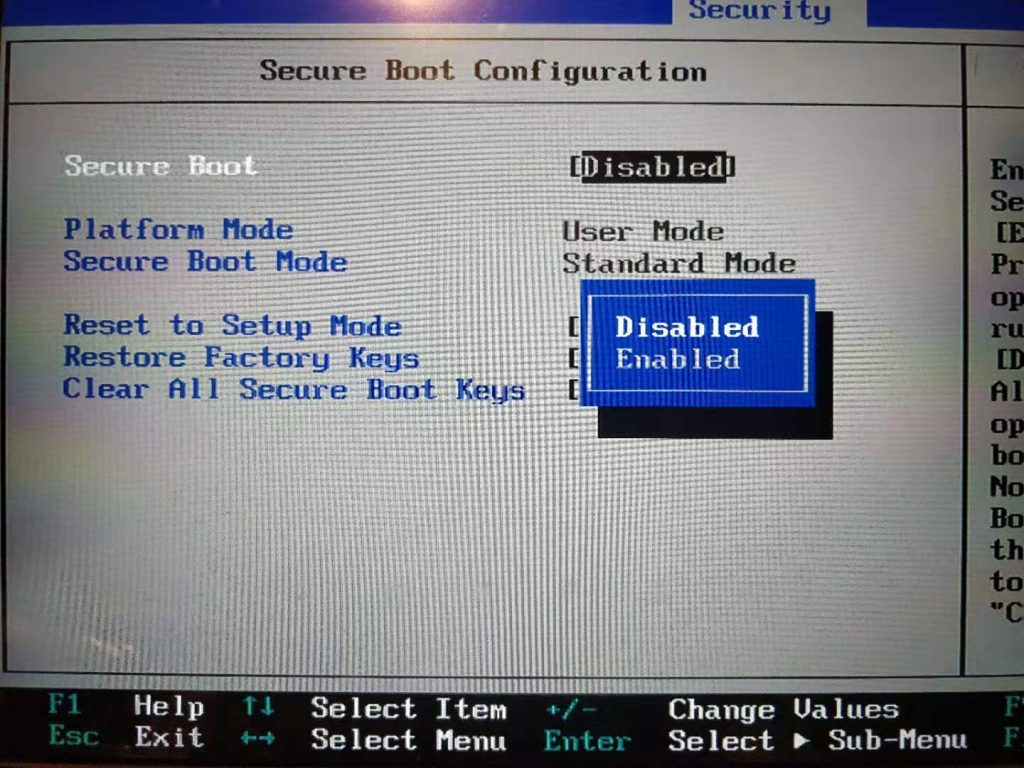
4. Disable Secure Boot in BIOS settings
In order to supoort VirtualBox running on Ubuntu normally, we should disable the Secure Boot feature in BIOS. Reboot the computer again, press F1 to enter BIOS settings, use arrow key to move to option "Security"--->"Secure Boot", and set the "Secure boot" option to "Disable". Press F10 to save and exit.
Conclusion
-
Using UEFI boot mode for both internal(Win 10) and external SSD(Ubuntu) has many merits:
- No need to enter the BIOS firmware to choose a boot device
- The Grub boot menu can manage the dual OS on both internal and external SSD
- No damage to internal SSD bootloader, Windows 10 can boot normally when the external SSD is removed.
-
Restrictions: If the external SSD is mounted on another computer, these merits above may not effect. As the other machine has different hardware/boot mode/partition table, etc.
References
The following links are related tutorials, but do not follow all of them, some steps should actually be changed according to your own computer's specifics.
Comments
Good guide to install Ubuntu ON an external drive. Thanks.